A demonstration is held to protest against U.S. President Donald Trump's decision to withdraw from the Paris Agreement, outside the White House in Washington D.C. June 1, 2017. (Xinhua/Yan Liang)
WASHINGTON, Jan. 19 (Xinhua) -- Donald Trump's fray with American scientists, which has been noted by Science magazine, is one defining aspect of his first year in the White House.
Such acrimony reflects the conflicting goals in this administration's scientific agenda, which proposed to start an ambitious plan like the Star Wars Program, but seems to show little respect for scientific facts that should underpin it.
DENYING CLIMATE CHANGE
Since taking office, Trump has rolled back many environmental rules, and called for deep budget cuts at key research agencies.
But the most disappointing thing is perhaps that, citing "draconian financial and economic burdens," he renounced the 2015 Paris climate accord, a hard-won international agreement to address climate change.
Dismissing global warming as false, despite all the evidence for it, Trump halted America's financial aid to the United Nations' (UN) climate change programs and issued an "Energy Independence" order last year, vowing to reinvigorate the coal industry but giving a cold shoulder to the renewable energy sector.
It remains unclear whether shirking its responsibility can help make America great again. Yet Trump's endeavor to rejuvenate a sunset industry may prove to be a lost cause.
Looking forward, the global drive to fight climate change is irreversible. The Paris accord has been already approved by over 170 signatory parties, whose greenhouse gas emissions accounted for nearly 90 percent of the total. Even within the United States, many states, counties and companies have pledged to continue cutting emissions.

Demonstrators take part in the March for Truth rally on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., on June 3, 2017. Sharp political passions over U.S. President Donald Trump's withdrawal from the Paris climate treaty and his alleged links to Russia brought people onto the streets of cities around the globe. (Xinhua/AFP)
Trump has not even until now appointed a director of White House Office of Science and Technology Policy, a job that can link the science community and the Oval Office. The director can also help the president to work out a science strategy.
"Since World War II, no American president has shown greater disdain for science -- or more lack of awareness of its likely costs," Neal Lane, a former science adviser to Bill Clinton, wrote in an op-ed article in the New York Times.
EMBRACING SPACE
As an apparent contradiction, his disdain for science is coupled with an ambition to restore America's glory in space. Trump ordered to rebuild the "National Space Council," which had been shelved for a quarter of a century.
On Dec. 11 last year, Trump announced that American astronauts would return to the moon before landing on Mars. "We will not only plant our flag and leave our footprint -- we will establish a foundation for an eventual mission to Mars."
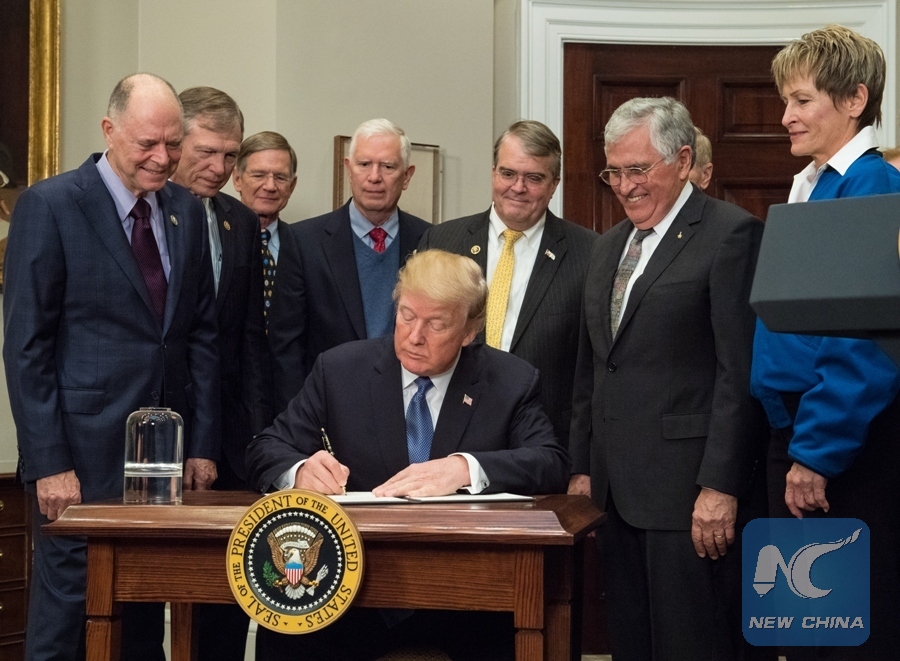

Photo released by NASA on Dec. 11, 2017 shows U.S. President Donald Trump (front) signing the Space Policy Directive 1 at the White House in Washington D.C., the United States, on Dec. 11, 2017. Donald Trump signed his administration's first space policy directive, formally directing the U.S. space agency NASA to send astronauts back to the moon and eventually Mars. (Xinhua/NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
Forty-five years after Americans landed on the moon, a signal of victory and strength in the Cold War era, Trump is playing with a new plan that would restore the national pride but potentially lead to a new space race.
Many are skeptical about the space plan's timetable and budget. Ten years ago, then President George W. Bush launched the "Constellation Program," vowing to send Americans back to the moon by 2020, but it was canceled by Barack Obama.
There is much uncertainty about how far Trump's plan can go as the government is on the brink of being shut down.
FLEXING MILITARY MUSCLE
Last August, Trump elevated the United States Cyber Command to the status of a full and independent Unified Combatant Command, a signal that the United States is preparing for a cyber war in the future.
A four-page memo told federal agencies that their research dollars should be focused on delivering short-term dividends, like in strengthening national defense and border security.
The blueprint prioritized the development of military technology including the development of missile defense capabilities, a modern strategic deterrent, hypersonic weapons and defenses, autonomous and space-based systems, trusted microelectronics, and future computing capabilities.
The memo has an explanation for the agenda: "Historically, federal R&D (research and development) investments in military technology have led to the development of breakthrough technologies that have improved lives beyond the battlefield."
One year ago, Trump defined our era in his inaugural address "at the birth of a new millennium, ready to unlock the mysteries of space, to free the Earth from the miseries of disease, and to harness the energies, industries and technologies of tomorrow."
One year on, however, he has created more disappointments and uncertainties.
"It's difficult to know what Mr. Trump really thinks about scientific issues of public concern," Lane said.

